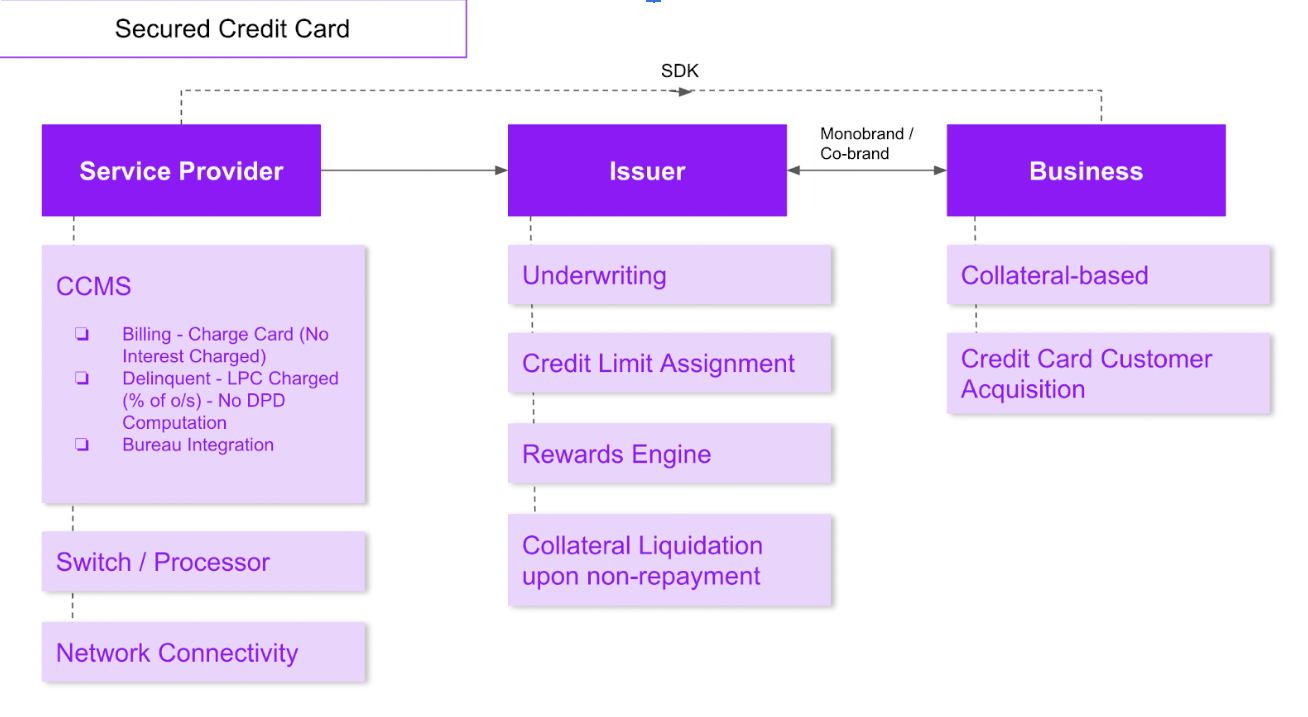
What is e-RUPI & and how it is a big leap in the Digital Payments Ecosystem in India
Launched in August 2021 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, e-RUPI is a new digital payment solution for seamless transfer of funds, without the need for any card, digital payments app, internet access or even a bank account.
e-RUPI is a cashless and contactless payment method done through an e-voucher sent to beneficiaries via QR Codes or SMS strings, which can be redeemed/used for specific purpose only, at the service providers. It connects the sponsors of the services with the users and service providers digitally, with no physical interface required.
These vouchers will be both person and purpose/end-use specific, for ex: If they are issued by government for availing any medical service at a particular hospital, then they can be redeemed only for that. In other words, it will work as a closed system PPI.
How e-RUPI works?
e-RUPI is developed by NPCI on its UPI platform, with onboarded banks as the issuers. The government or any private corporate will approach the partner banks with the details of specific beneficiaries to whom the payments have to be made and the purpose of such payments.
Each beneficiary will be uniquely identified basis their mobile number and voucher will then be issued and delivered (in the form of QR Code/SMS) in the name of that beneficiary only.
Objective of e-RUPI
e-RUPI is expected to serve the following objectives:
- The long-term vision of e-RUPI is to reach the unbanked population, include them into a formal financial system and reduce the digital gap in the country
- To provide an equal access to various healthcare, education, and other benefits to each citizen of the country
- Transparency in transactions, as the end-use of the funds can be easily tracked
- Will guarantee that the money is used for the purpose for which it was intended, unlike traditional bank account transfer where it is possible that the funds are used for other purposes
Further, with the government in the process of establishing a digital currency for the Central Bank, e-RUPI can be used to emphasize the flaws in the current digital payment infrastructure which is crucial for the development of digital currencies in future.
Application of e-RUPI
Currently, this is a platform launched as a government initiative for leak-proof distribution of welfare benefits to eligible beneficiaries. It aims to provide services under various schemes of the government including Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana and other subsidy programs, etc.
However, in future even private entities can use this voucher-based payment method for providing services to their employees for travel, healthcare, and other such purpose-specific expenses.
It can also be used to provide credit to first-time borrowers, where the end-use of funds is specific and thereby evolving the digital lending landscape in the country.
A move towards digitalization and introduction of Digital Currency
While e-RUPI is in itself not a digital currency, as it is still backed by Indian Rupee as the underlying asset and is purpose specific, it is definitely a move towards introducing digital currency/cryptocurrency in India.
Both e-RUPI and cryptocurrency work on similar principle of enabling end to end digital transactions and removing physical intermediaries thereby ensuring transparency, data security and overall reduction in operating costs.
What lies ahead?
With the introduction of e-RUPI, it is clear that the government is in support of new digital initiatives, as they expect that India has tremendous potential to change the way they transact and pay for different services. This is supported by increasing adoption of digital payments for small-value transactions, especially by the non-digital customer segment in the country.
This backed by India’s high currency to GDP ratio, validates that such digital initiatives and crypto assets/digital currencies can co-exist and position India as the front runner towards forming a complete digital economy. Further, e-RUPI will encourage the use of PPIs in India for better channelization & monitoring of funds, providing an opportunity for Fintechs driving digital payment solutions to design new products build around e-RUPI/digital currencies and such kind of digital solutions.