SWIFT gpi- Future of Cross Border payments
Cross-border payments have traditionally remained a mystery for most users except the participating banks. These payments go through a series of banks before getting credited to the recipient’s account. SWIFT is the primary method of communication used by banks in processing international payments.
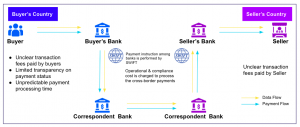
In the era of the global digital economy, cross border payments are still felt backward and rigid. One of the most common challenges of cross border payment today is that it takes several days or a week for funds to reflect in the receipt’s account. This can be due to several reasons such as compliance requirements, regulatory differences, or high number of intermediary banks. Each participant of the entire value chain of the transaction is limited to its own data environment. Lack of visibility of payments status and control on payments affects both the parties involved in the transaction and their banks. Additional challenges in terms of High cost and uncertainty of fees to be charged leading to reconciliation issues also leaves bad customer experience.
To solve the challenges faced by banks and cater to the changing need of corporates, SWIFT has launched new initiative- SWIFT global payments innovation (SWIFT gpi)
SWIFT gpi at a Glance
With SWIFT gpi financial institutions can send or receive funds quickly and securely across the world, with full transparency and traceability over the payments at any point in time. It aims to improve the cross-border payments across the correspondent bank and introduce a new market standard by connecting all the participants of the payments in the value chain.
How does it work?
SWIFT gpi is a cloud- based database that is hosted at SWIFT, designed to provide complete end-to-end visibility of the payments status until it reflects in the receipt’ account. SWIFT gpi seeks to meet the changing needs of corporates – faster transactions with full transparency and complete end to end traceability, without compromising banks’ ability to meet compliance obligations and market, credit and liquidity risk requirements.
To track the transaction payment, the initiating bank can assign a unique tracking code corresponding to that particular transaction. This unique code is 32 hexadecimal characters. This code is used further to track the status of the payment in the payment value chain using SWIFT gpi.
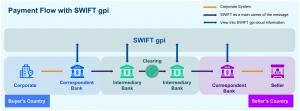
SWIFT gpi combines traditional SWIFT messaging and banking systems with new business rules. To ensure consistency, SWIFT gpi operates based on business rules captured in the multilateral service level agreements (SLA) between participating banks.
Benefits to corporates
SWIFT gpi is an initiative to improve the customer experience in cross-border payments by connecting all the stakeholders of the value chain. Its design helps banks to complete the international payments faster and without friction which will indirectly help the corporates to expand and grow their business globally. Main benefits for corporates:
- Same day transaction which was almost a week earlier.
- Transparency in the fees charged with respect to commission and exchange rates.
- End to end tracking of payment status at any point in time via the cloud using a Unique reference number.
- The transmission of full and unaltered remittance information which will ease the reconciliation of payments for the corporates.
- Cloud improves the communication between all the parties involved in the value chain.
Benefits to Financial Institution
With the implementation of the first phase of SWIFT gpi, banks can provide better end to end experience to its customers which will improve bank’s relationship with its clients and motivate these clients to increase their volume of transactions with SWIFT gpi banks only.
Cloud technology has eased the bank’s workload in terms of engaging employees for tracking the payments for clients and improving the operational efficiency of the bank. In the long run SWIFT gpi will help banks achieve higher cost saving and operational efficiencies from enhanced compliance practices and optimised intraday liquidity flow.
Correspondent banks benefit strategically by leveraging the end to end digital ecosystem provided by SWIFT gpi and connect all the parties involved in the value chain of international payments.
Roadmap for Implementation
For smooth adoption of SWIFT gpi, it is being rolled out in three phases. First phase was launched in Feb 2017 with a new set of standards in cross-border payments to improve speed, transparency over fees and end to end tracking of payment information to all stakeholders. Second and third phases would be related to high cost and operational inefficiency in the current cross- border payments landscape.
In the second phase, more control will be given to banks on payments. In case of any fraudulent activity, the bank can immediately cancel the payment regardless of the status of payment in the payment chain. Also, participants can send additional information along with the payment if required.
SWIFT has introduced SWIFT gpi tracker to improve transparency and traceability in the international payment value chain. This tracker can easily be integrated with back-end systems of banks.
These phased rollouts and the approach taken should make it easier to adopt across banks and payment networks resulting in unravelling the mystery around cross-border payments.