Enhancing Security and Transparency: A Comprehensive Guide to Issuer-Led Tokenization
In today’s digital era, the security of financial transactions is of utmost importance. With the rising prevalence of cyber threats and data breaches, it’s crucial for financial institutions to adopt robust security measures to protect sensitive card information. One such innovative solution gaining traction is issuer-led tokenization. Let’s explore what issuer-led tokenization is, how it works, and why it’s important, all explained in straightforward terms.
Understanding Issuer-Led Tokenization:
Issuer-led tokenization is a sophisticated security measure designed to safeguard sensitive card data during transactions. Unlike traditional methods of storing card details, tokenization replaces this information with unique identifiers, known as tokens. These tokens retain the essential characteristics of the original data but are meaningless to unauthorized parties. In the context of card on file (CoF) transactions, issuer-led tokenization ensures that card data is securely stored and transmitted, minimizing the risk of data breaches and fraudulent activities.
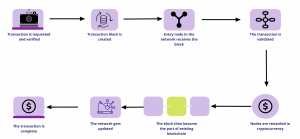
Process of Issuer-Led Tokenization:
- Token Generation: Card issuers generate unique tokens for each cardholder, securely storing them on devices and issuer systems.
- Customer Consent: Before tokenizing card data, card issuers obtain explicit consent from the cardholder, ensuring transparency and accountability in the tokenization process.
- Tokenized Transactions: During payments, meaningless tokens are transmitted instead of sensitive card details, ensuring security and confidentiality.
- Secure Storage: Encrypted tokens and card details are securely stored, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Compliance with Regulatory Guidelines: Issuer-led tokenization adheres to regulatory guidelines, including restrictions on storing actual card data and requirements for explicit customer consent.
Significance of Issuer-Led Tokenization:
Issuer-led tokenization offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced Security: By replacing sensitive card data with tokens, issuer-led tokenization strengthens the security of card transactions, reducing the risk of data breaches and fraudulent activities.
- Transparency and Accountability: Explicit customer consent and adherence to data storage guidelines promote transparency and accountability in the tokenization process, fostering trust between cardholders and issuers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with regulatory guidelines ensures that card issuers maintain the integrity and security of card data, mitigating potential risks and liabilities.
Issuer-led Vs Acquirer-led tokenization:
Tokenization, whether led by the issuer or the acquirer, serves as a crucial security measure in today’s digital payment landscape. When led by the issuer, tokenization involves the replacement of sensitive card details with unique tokens, enhancing security and protecting cardholder information during transactions. On the other hand, when led by the acquirer, tokenization offers merchants flexibility by allowing them to manage tokens and streamline payment processes. While issuer-led tokenization prioritizes security and cardholder control, acquirer-led tokenization focuses on merchant convenience and transaction efficiency. Both approaches contribute to a safer and more secure digital payment ecosystem, ensuring trust and reliability for all parties involved.
In Conclusion:
Issuer-led tokenization represents a significant advancement in the security and transparency of digital payments. By incorporating explicit customer consent and adhering to regulatory guidelines, card issuers can enhance the security of card transactions while maintaining transparency and accountability. As digital payment ecosystems continue to evolve, issuer-led tokenization emerges as a key strategy to safeguard sensitive card information and uphold the integrity of financial transactions.
Authored by Astha Bishnoi, Manager – Partnership & Sales at CARD91