Digital Currency: The future of the Global Payment System
Digital currency would shift the world’s economy towards a cashless economy. Digital currency has the capability to change the perspective of individuals towards money. The continuous rise of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum has led the global central banks to explore the benefits and challenges of a regulated Digital Currency – Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC). Few countries have even started work on the same and most of them are at the R&D stage and China is in the pilot stage of CBDC.
What is Digital Currency?
The Digital currency has all the intrinsic properties of cash/ physical currency except the form. Cash/Physical currency has both physical and electronic form, however Digital currency exists only in electronic form. Digital currency can be accessed with computers or mobile phones. Digital currencies can be used to purchase goods or pay for services like cash/physical currency. For example, Instead of using cash or making e-payments, customers can make the payment to retailers by transferring digital currency using a mobile phone.
Success Stories from the Past
In the early 80s, all the trading of equity stocks and the Government securities was done offline through paper-based certificates but in today’s world of technology, all the trading of stocks and government bonds is being done only digitally. The digitalisation of the complete trading process has been seamless and created more growth opportunities and transparency. Similarly, digital currency can remove the intermediaries and perform direct peer to peer transactions with higher speed, accuracy, transparency and traceability.
Distributed ledger technology-based cryptocurrency such as Bitcoin, Ethereum exist and are being used around the globe. Their production is completely digital and is not regulated by any government authority or central banks. Central banks around the world are also researching regulated digital currency (CBDC).
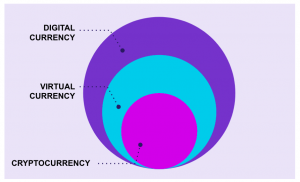
How Digital currency differs from Virtual and Cryptocurrency
From a broader perspective, virtual and cryptocurrency are subsets of Digital currency. Virtual currency is an unregulated digital currency mainly controlled by its developer, the founding organisation, or the defined network protocols such as cryptocurrencies and coupon- or rewards-linked monetary systems.
Virtual currency that uses cryptography to secure, control and manage the creation of new currency units and finally verify the transactions is commonly known as cryptocurrency. Bitcoin and Ethereum are the most popular decentralised cryptocurrency and Facebook’s Diem is an example of centralised cryptocurrency.
Concept of CBDC and how it would work?
Digital currency that will be issued and regulated by the country’s central bank is known as a central bank digital currency (CBDC). For example, think of a cryptocurrency being managed and backed by the full faith and support of the country’s central bank like RBI in the case of India. This cryptocurrency would be stated as CBDC. At present, no central bank across the world has its own digital currency.
CBDC would work in a similar fashion as the cash/ physical currency. Only difference is that, once a payment is made using CBDC then the counter-party can neither cancel nor reverse the transaction, However, in regular online payment, such transactions can be reversed and cancelled. This is because CBDC uses blockchain technology which does not let users make alterations in past transactions. This is one of the key features of Digital currency. CBDC would be legal in the country and can be used for any purpose.
Benefits of Digital currency
Faster payments – All inbound and cross border transactions gets completed on a real-time basis
Cost-effective– Digital currency reduces intermediaries in peer to peer transactions especially in the case of cross border payments causing significant reduction in terms of fee charged.
24*7 Accessibility– At present, Post working hour financial transactions take more time but with digital currency, the transactions can be performed at any time with the same speed.
Transparency & Traceability – Digital currency brings more transparency and easy traceability of transactions to all the parties involved in the financial transactions particularly in the case of cross border transactions.
Support for unbanked or underbanked– CBDC helps all unbanked individuals to pay bills and make payments online using the digital currency with no extra charges.
More efficient government payments– It also helps governments to make the payments to individuals in a quick and seamless way especially in the case of an emergency like the Covid-19 pandemic. It is very difficult to help the gig workers financially in this situation when lockdown is imposed everywhere and no source of earning for them. Digitally currency (CBDC) would have helped them by enabling governments to transfer the fund on a real time basis even in case of unbanked workers.
Digital currency Disadvantages
High efforts to learn how to use digital currency- To learn all the basic tasks of digital currency like how to open a wallet account, store digital currency is a bit challenging especially for uneducated or illiterate users.
Blockchain transactions can be expensive- Current digital currency like Bitcoin uses blockchain where electricity cost is very high because computers are used to solve complex equations to record and perform the transactions. Cost charged Per transaction, independent of transaction value so it is not an efficient option for small value transactions.
The large swing in digital currency price- Current digital currency value is very volatile due to consumer sentiment and psychological triggers. However, CBDC is expected to be more stable like current fiat currency.
Developing CBDC is a very time-consuming process – Currently global central banks are exploring the opportunities with CBDC and even if some central banks decide to create CBDC, it would be very costly and time consuming to develop, implement and replace the current Fiat currency.
In countries like ours which is predominantly a cash dominated economy where most SME and MSME transactions are done through either cash or cheques. The anonymity and untraceability of cash transactions make it even more challenging to completely accept digital currency (CBDC) in India.
However, India has always been ahead of other countries in terms of adoption of technology and digitization. So, Now is the time for our central bank to start exploring the opportunities in central bank digital currency to launch the World’s first CBDC.